How to Secure a Wireless Network
by ythao907 in Circuits > Computers
1503 Views, 3 Favorites, 0 Comments
How to Secure a Wireless Network

We will be learning how to access the router's web interface and how to utilize settings from the manufacturer to help secure wireless network. Here is a list of things that are covered in this document:
- How to access the router
- Establishing strong passwords
- Mac address filtering
- Firmware upgrade
- Encryption
- Guest Network
- Troubleshooting
Finding the IP Address
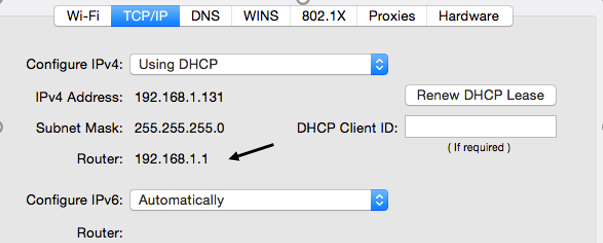
Find the IP Address provided by the router's manufacture to access its web interface. In the following steps, are detailed information on how to find the IP address for both MAC and Windows users.
For MAC computer
a.
b.
c.
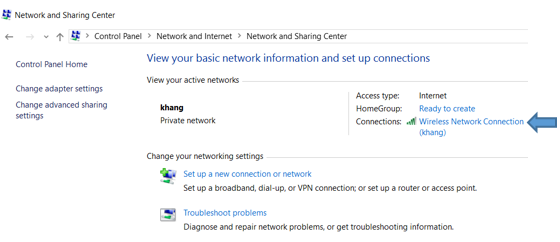
For Windows computer
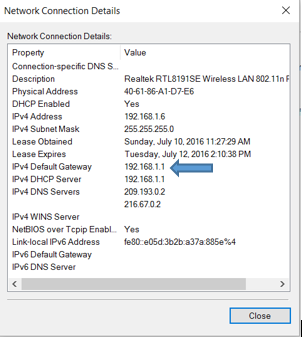
a. Open the Network and Sharing Center in the Windows Control Panel. Click the name of your Internet connection.
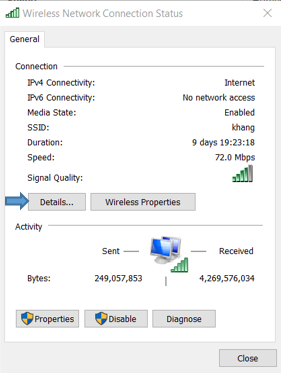
b.Click on the details button to view more about the connection.
c. Look for default gateway
Accessing the Router’s Web Interface
a. Open a web browser
b. Type the router's IP address into address bar, press enter.

c. This will bring you to the log in screen for the router.
d. For first time login, usually, the username is admin and the password is ether password or admin. (If that is not the case, look up the make and model of the router to find the default username and password)

Configuring Wireless Security Settings (Please Note: Location of Settings May Vary)
1. Create a unique password for the router
It is recommended to change your default administrator password. In some cases, routers are shipped out with no password. This is the password that allows you to the router’s web interface, not to get confuse with your WIFI password. This setting is usually found in system settings or management.

Passwords in length of 14 key is highly recommended with the use of special key such as !@$#%^* and upper and lowercase. Your password does not have to be difficult and can be repetitive. For example, you can do @William12William!
2. Upgrade your router’s firmware
Firmware updates contain improvements and fixes to problems that may have existed. To do this, click on check firmware, usually found under system or management.

3. Change your network’s SSID name
It is recommended to change your network name from default, this is also known as Service set identifier (SSID). This is the name of your WIFI.
To do this:
a. Open tab “Wireless”.
b. Click “Basic Wireless Settings”. Change where it says “Network Name (SSID):”

c. Here you have the option to hide your network. By clicking disabled SSID broadcast, the network name will no longer appear in the list of networks that appear when a wireless device runs its scan. New devices must be manually configured to be able to find the wireless router the first time.
More Wireless Security Settings
4. Enabling encryption
It is strongly suggested to utilize WPA2 as your security mode to protect your network. WPA2 is the most secured and up to date.
To do this: click on the tab “Wireless”. Then “Wireless security” or " Basic Settings". Select WPA2

5. WIFI Password
In the wireless security tab, in Passphrase or presharekey, enter your password. Again, passwords of 14 key in length including special keys is recommended. This is the password to login to your network/wifi and not your router's interface.
6. Disabling the guest network.
a. Go to tab “Wireless” and choose “Wi-Fi Protected Setup”.
b. By clicking no, guest access will be disabled which is recommended for security purpose.

c. If you want to keep guest network, modify the settings for more secure connections.
7. Filter MAC-Addresses
Every wireless device has their own unique id called mac-address. Mac address filtering allows only specific addresses to connect onto the network.
A. To find the mac address of a PC, in the start menu (bottom left corner of your screen) click and search command prompt.

B. Type in ipconfig /all
C. Look in the description field for wireless. The Physical Address for that block is your wireless MAC address.

D. Enable the wireless Mac Filter option and input the mac address in the filter list. This list allows only the specific Mac Addresses to be on the network.

Troubleshooting
1. No power
a. Make sure the cord is plugged
b. Check outlet for power source
c. Check for damage cord
d. Could be hardware problem if all else failed
2. No internet
a. Power off the router.
b. Wait 5-10 minutes.
c. Power on the router and modem.
d. If the problem persist call the internet provider.
3. How to reset your router in web interface.
a. Click “Administration” tab; click “Factory Defaults”.

4. Forgotten password
a. Find the reset button at the back of the router, press and hold the button for 10 seconds. This resets your router to factory settings.